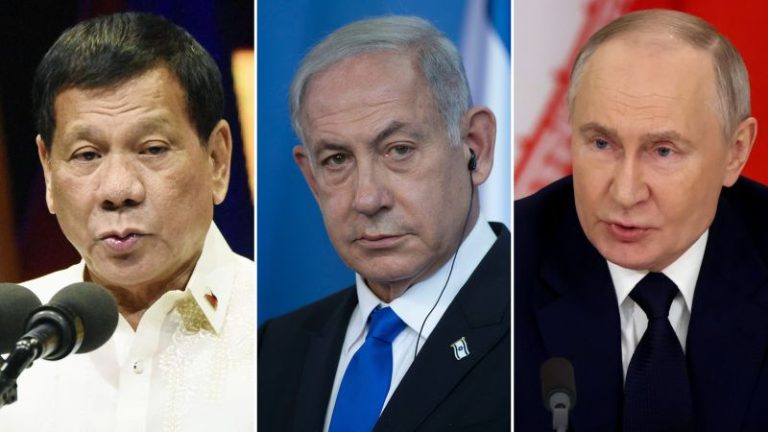
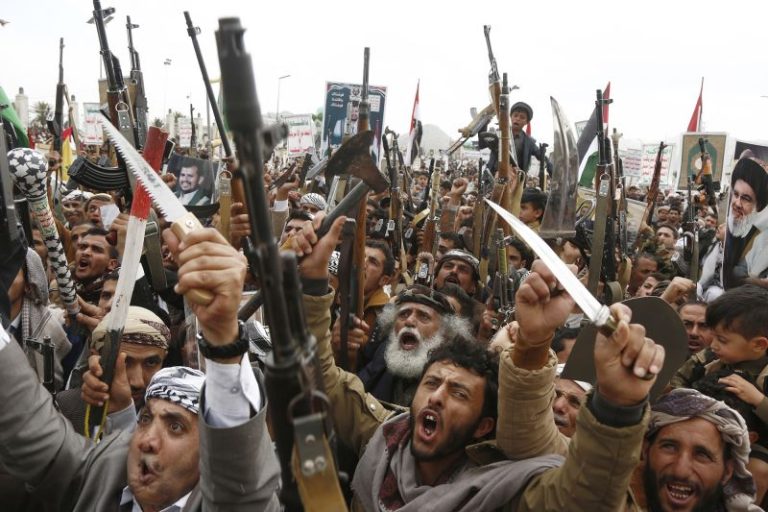
The dramatic arrest of the Philippines’ controversial former president in March sent shock waves through much of the world – and cast a renewed spotlight on the other leaders wanted by the International Criminal Court (ICC).
Former Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte, who was whisked off to the Netherlands to answer for alleged crimes against humanity, had long been under scrutiny over a brutal anti-drugs crackdown. But even after years of on-and-off investigations, during which Duterte taunted the court and told it to “hurry up,” his detention came as a surprise to many experts.
“We have had other high-ranking individuals brought before the court,” including several former presidents of African nations, said Leila Sadat, professor of international criminal law at the Washington University School of Law and the former special adviser on crimes against humanity to the ICC prosecutor.
But in many of those cases, the prosecuted leaders were either summoned to court or arrested after a warrant was publicly issued – a stark contrast to Duterte’s case, where the warrant was issued secretly and the former leader swiftly apprehended within several head-spinning hours.
“It’s the first time we’ve seen this at the ICC,” Sadat said – though similar cases have been seen in other international tribunals, she added.
Duterte, now 80, oversaw a ferocious crackdown on alleged drug pushers in the Philippines that killed more than 6,000 people, based on police data. Independent monitors believe the number of extrajudicial killings could be much higher.
His arrest is significant, partly because it could set a precedent for future trials of other leaders wanted by the court, however unlikely, including Russian President Vladimir Putin and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu.
That’s not to say their turn could be imminent, far from it – many political factors can make it extremely difficult to execute an arrest warrant.
Case in point: Netanyahu on Sunday was wrapping up a visit to Hungary, in defiance of the ICC warrant. As a signatory to the Rome Statute, Hungary is obligated to arrest anyone wanted by the ICC. Instead, its Prime Minister Viktor Orban welcomed Netanyahu with open arms, and Budapest announced it would begin the process of leaving the court.
But Duterte’s case has shown that arrest is possible – especially once a leader is out of office – and that the threat against those wanted leaders is not only theoretical.
“The precedent set here – maybe not now, but in future generations – will allow us to visualize what justice looks like for the highest-ranking leaders of countries that commit these kinds of crimes,” said Gregory Gordon, a professor of international criminal law at the Peking University School of Transnational Law in Shenzhen, China.
“There’s always that initial breakthrough that has to happen.”
Putin and the Ukraine war
Located in The Hague in the Netherlands, the ICC investigates and prosecutes individuals for war crimes, crimes against humanity, genocide and crimes of aggression against the territory of its member states, of which there are 125.
The court cannot carry out arrests on its own and relies on the cooperation of national governments to execute warrants – which often rests on domestic politics and political will.
ICC member countries include Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, Australia, Brazil and all other members of the European Union – at least until Hungary makes its promised exit.
In March 2023, the ICC issued an arrest warrant for Putin and Russian official Maria Lvova-Belova over an alleged scheme to deport Ukrainian children to Russia.
The charges were the first to be formally lodged by the ICC against Russian officials since the Kremlin’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine began in 2022.
Russia – like the United States, Israel, China and Ukraine – is not a member of the ICC. The court does not have its own police force and does not conduct trials in absentia – and therefore the likelihood of any Russian official appearing before it is very low, analysts said.
Any charged Russian officials would either have to be handed over by Moscow, or arrested outside of Russia, said Sadat, the Washington University professor.
“The warrant against Vladimir Putin himself is obviously the most challenging because he’s a head of state in power, and he’s not going to leave Russia unless he’s pretty sure he’s going to have immunity wherever he goes,” she said. “But his choices are now restricted, and he’s been labeled, for better or worse, a war criminal.”
Gordon agreed, saying the chances of Putin being arrested are slim, given his “firm grip on power” and layers of protection – unless Russia’s domestic political situation changes enough to leave him vulnerable. After all, it was a dramatic change in the Philippines’ domestic politics that ultimately did for Duterte.
Even when Putin leaves Russia, many countries are unwilling to arrest him. Last year, the Russian leader traveled to Mongolia without facing any repercussions – despite the East Asian country being a member of the ICC.
“Obviously the pressure on a small country like Mongolia is pretty substantial,” Sadat said.
But she pointed to other times the warrant had seemed to restrict Putin’s movements; in 2023, the Russian leader attended a BRICS summit in ICC signatory South Africa via video call, sparing the host country a potential diplomatic quandary.
“I think the warrants themselves are powerful. At the same time, we do have to see a significant number of warrants actually get executed, or the warrants become sort of symbols of a court that can’t arrest its accused,” she said.
“That’s why (Duterte’s arrest) is a really exciting moment for the court, because it shows it can engage in interstate cooperation.”
Netanyahu, Hamas and the Gaza war
The ICC issued its warrant for Netanyahu in November 2024 – also seeking the arrest of former Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant – citing allegations of war crimes and crimes against humanity committed during Israel’s war against Hamas in Gaza.
A senior Hamas official is also wanted by the ICC on allegations of war crimes and crimes against humanity committed during the October 7, 2023 attacks on Israel. Other leaders of the militant group sought by the court for prosecution were killed by Israel.
The historic warrants made Netanyahu the first Israeli leader summoned by an international court for alleged actions against Palestinians in the more than seven-decade-long Arab-Israeli conflict.
The warrants were also denounced across the Israeli political spectrum as unconscionable, with Netanyahu’s own office labeling the move “antisemitic.” Several Israeli allies – including the United States – strongly criticized the ICC warrant.
Israel is not a member of the ICC and does not recognize the ICC’s jurisdiction, nor does it honor international warrants issued by the court, and likely wouldn’t turn over Israeli citizens for prosecution. In addition, the ICC only steps in when a country’s own government is unwilling or unable to prosecute cases.
But unlike Russia, it is a functioning democracy, with a long history of peaceful transitions between elected governments. That makes Netanyahu’s future political security more tenuous than Putin’s, and more comparable to the Duterte situation, where a shift in government once the Philippine leader was out of office ultimately led to his downfall.
The Israeli prime minister is already contending with a number of domestic legal troubles unrelated to the Gaza war, including a long-running corruption trial.
Israel is also deeply politically divided, with many citizens furious at the Netanyahu government and his far-right cabinet allies.
According to Gordon, it is at least “conceivable” that Netanyahu could one day face arrest in Israel for alleged crimes related to Israel’s actions in Gaza – though that still doesn’t mean the ICC warrant would be enforced.
Then there’s the fact that several powerful nations have opted not to enforce the ICC’s warrants while others have openly rejected them – further undermining the court’s authority.
France, for instance, had fervently supported the ICC’s warrant for Putin – but it shifted its stance after the court sought Netanyahu’s arrest, arguing that as Israel was not an ICC member, its prime minister should be immune from prosecution. Other European nations have also indicated they would be unwilling to enforce the Israeli warrants.
But critics say the responses suggest two sets of rules: one for the West’s traditional allies, and another for its foes.
The ICC has a long list of outstanding arrest warrants, including for former dictator Omar al-Bashir, who ruled Sudan for three decades before being deposed in 2019. Currently imprisoned in Sudan, Bashir faces charges of genocide, war crimes and crimes against humanity in Darfur.
A disproportionate number of ICC prosecutions have been against African leaders, warlords and militia members – including former Kenyan President Uhuru Kenyatta and the East African country’s current leader William Ruto, whose case was abandoned by the court partly due to “witness interference and political meddling.”
The ICC’s past focus on Africa is partly rooted in its constitution, said Sadat in Washington. The court can only exercise jurisdiction in crimes committed on or after its creation on July 1, 2002. At the time, major wars that killed millions were raging across Africa, from Darfur to the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Additionally, many African nations self-referred their cases to the ICC, Sadat added – meaning they asked the international court to investigate and granted it jurisdiction.
“With time, the prosecutor’s office started staffing up, developing more expertise, taking on additional situations … now the court is moving into other situations,” Sadat said.
But, she added, it’s difficult to prosecute alleged crimes while conflicts are ongoing and those accused remain in positions of power.
For years, the ICC has faced criticism for slow trials and its low conviction rate. From 60 arrest warrants issued since the court was created, 31 suspects remain at large. Only 11 defendants have ever been convicted – all African war criminals.
Sadat pointed to Syria, saying that for years, the ICC couldn’t “figure out a way to get jurisdiction” to investigate alleged war crimes during the country’s civil war – until former dictator Bashar al-Assad’s regime was toppled in December. Since then, the new interim government has invited the court to visit the country and collect the evidence needed for prosecution.
The Philippines is another prime example of how ICC cases often become stuck until some political upheaval changes the game, said Gordon, the law professor.
Philippine President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. had previously said the Southeast Asian country would not engage with the ICC, only for Manila to reverse its stance this week following the collapse of an alliance between the Marcos political dynasty and Duterte’s clan.
Some might argue “that this is just about politics, and that the only time the ICC will ever be able to engage in the justice process is if political processes are aligned in certain ways – and it’s just a matter of luck, not justice,” Gordon said.
Duterte’s arrest could establish a foundation for “combating the culture of impunity and assuring accountability for state leaders who commit international crimes,” Gordon said.
“That makes people in the future more comfortable with the idea that it can be done.”
This post appeared first on cnn.com