Chinese warships have been circumnavigating Australia’s coastline for more than three weeks, passing within 200 miles of Sydney, and staging unprecedented live-fire drills on its doorstep with New Zealand.
The exercises, which came without formal notice, has deep caused consternation in both nations. Suddenly, the specter of China’s military power was suddenly no longer confined to the distant waters of the South China Sea or the Taiwan Strait – where China’s territorial aggression has escalated under leader Xi Jinping – but a stark reality unfolding much closer to home.
At the same time, Chinese warships have been sighted near Vietnam and Taiwan, part of a show of Chinese naval strength in the Pacific region that regularly rattles US allies.
China was unapologetic and insisted it complied with international law, with state media suggesting Western countries should get used to Chinese warships in nearby waters.
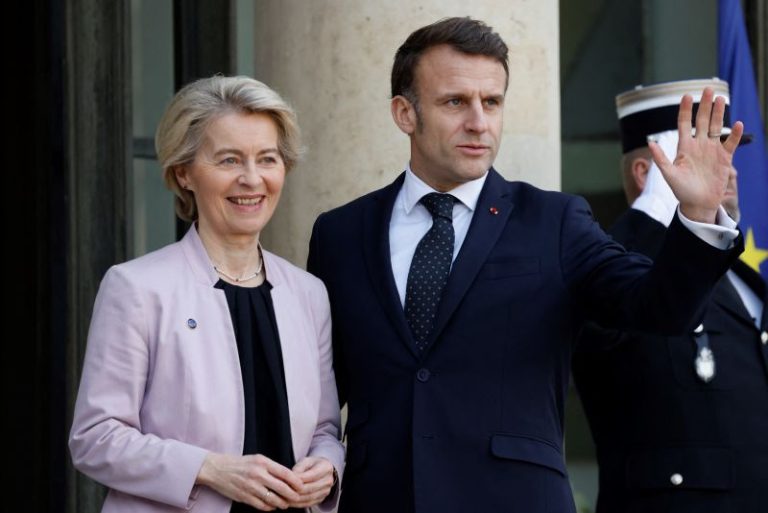
In the past, Washington’s partners have found comfort in their firm ties with the US, but that was before Donald Trump’s explosive meeting with Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky, and the US leader’s subsequent order to halt aid to Ukraine as it battles Russia’s invasion.
The bust-up in the Oval Office served to sharpen anxieties in capitals across the Pacific: If the US is willing to turn its back on Ukraine – effectively rewarding Russian President Vladimir Putin’s aggression in Europe – would it do the same in Asia when faced with a belligerent Beijing?
Trump’s embrace of Russia and his cold shoulder to Europe – driven by a transactional approach that Singapore’s defense minister likened to a “landlord seeking rent” – has heightened trepidation in the Indo-Pacific region, where many nations look to the US to keep Chinese aggression in check.
“It does raise issues as to whether the US will be committed to regional security. And even if the US remains committed, what will the Trump administration ask in return?” said Collin Koh, research fellow at the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies (RSIS) in Singapore.
Experts say it’s a fair question from allies who’ve long relied on the US to provide security assurances, enabling them to limit their own defense spending.
Now might be the time, they add, for American partners, like Australia and New Zealand, to reexamine budgets and tighten regional alliances with other countries that could find themselves exposed as Trump pursues his “America first” mantra.
Australia has made sure the world is aware of China’s movements in international waters in the South Pacific, issuing daily location updates from trailing Australian Navy ships and spy planes.
Defense Minister Richard Marles said the data would be analyzed to determine exactly what China was doing – and what message it was intending to send.
China’s ambassador to Australia, Xiao Qian, maintained that China posed no threat to Australia while signaling that more warship visits should be expected. “As a major power in this region…it is normal for China to send their vessels to different parts of the region to conduct various kinds of activities,” Xiao told Australia’s public broadcaster the ABC.
Across the Pacific in Washington, Trump was sending his own message to US partners in Europe that they needed to step up military spending in defense of Ukraine.
Before his fractious meeting with Zelensky, Trump had intended to sign mineral resources deal with the Ukrainian leader so that the US could recoup some of the cost of its aid to Ukraine since Russia’s invasion. But the signing ceremony was abandoned, with Trump telling Zelensky on his social platform Truth Social to “come back when he is ready for Peace.”
By subsequently cutting off military aid to Ukraine, Trump was seeking to force rich European nations to shoulder more of the load, say experts.
“He believes they have all been free riding off the United States for half a century,” said Peter Dean, the director of foreign policy and defense at the United States Studies Centre at the University of Sydney.
The move seemed to reap rewards when on Tuesday the European Union unveiled a plan to allow member states to borrow €150 billion ($158 billion) to boost their defense spending and “massively step up” their military support for Kyiv.
Dean says Trump wants a deal for peace in Ukraine; however, he’s ignoring Zelensky’s concerns about the longevity of that peace without measures to keep Putin in check.
“It seems to be that (Trump) almost wants peace at any price, rather than a peace that is fair and equitable, or a peace that you keep,” he said. “The question is, what does the deal look like? And that’s what everyone’s worried about. How much is he willing to trade away?”
As Trump upends the transatlantic alliance – a pillar of Western security for decades – his administration has signaled that the US should wrap up conflicts elsewhere to focus on deterring China in the Pacific.
The urgency of that aim was highlighted by China’s latest flexing of its military muscle.
“It’s a test of resolve, for sure,” said Drew Thompson, a senior fellow at RSIS in Singapore, of China’s military drills. “China (is) carving out a sphere of influence in the Pacific to test to see if countries in the region are going to resist it.”
Even before Trump’s clash with Zelensky, the presence of Chinese warships on its southern coast had turned Australia’s attention to AUKUS, its multibillion-dollar security deal with the US and the United Kingdom.
Concerns had flared about whether the deal could withstand the whims of Trump’s White House when a British reporter asked the US president if he and his UK counterpart had spoken about AUKUS.
“What does that mean?” Trump replied. The incident was later brushed off by Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent as an issue of accents. “I think we’re going to have to limit the questions to Americans he can understand,” he said.
Dean, from the University of Sydney, said it’s no bad thing that Trump wasn’t across the acronym because the deal already has the fulsome support of his closest advisers.
That support was cemented by Australia’s first down payment of $500 million to bolster America’s submarine production, with the agreement that some nuclear-powered subs will be sold to Australia to boost its military capability in the Indo-Pacific.
It’s the kind of deal Trump will want to focus on in the future, Dean said.
“He’s looking to make money for the United States, and he’s looking to do better deals. And AUKUS is a bit of an exemplar deal for them,” Dean said.
“For the Europeans, I wouldn’t underestimate Donald Trump looking at this and going, if the Australians can do this, why can’t you?”
Elsewhere across the Pacific, US allies appeared unsettled by the extraordinary scenes in the Oval Office.
Japan’s Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba struck a cautious tone on Monday, insisting he had “no intention of taking sides” when asked about the Trump-Zelensky clash.
Yet, he vowed to do his utmost to “maintain US involvement and promote unity” among the Group of Seven nations – hinting at growing disquiet over the fracturing of the Western alliance.
“Today’s Ukraine could be tomorrow’s East Asia,” he added. “We must also consider steadily increasing our deterrent power to prevent war.”
Japan, which has territorial disputes with China in the East China Sea, has raised concern about increasing Chinese military maneuvers in its nearby waters. Last year, a Chinese aircraft carrier entered Japan’s contiguous waters for the first time.
South Korea, another US ally in East Asia, declined to comment on the meeting between Trump and Zelensky but said it was closely monitoring US suspension of military aid to Ukraine.
Trump has repeatedly called on allies like South Korea to pay more for US troops stationed on their territory. In a speech to Congress on Wednesday, he once again made a veiled threat while referencing what he called unfair tariffs South Korea places on US goods – something Seoul denies.
“We give so much help military and in so many other ways to South Korea. But that’s what happened, this is happening by friend and foe,” Trump said.
In Taiwan, the self-governing democracy China has vowed to one day absorb, Defense Minister Wellington Koo tried to reassure confidence despite what he described as “rapid and bizarre changes” in the international landscape.
“I think the United States won’t retreat from the Indo-Pacific region, because this is its core interests,” he told reporters in a briefing Tuesday, citing shared interests with Washington in economic development, geopolitics and US military security.
But Koo also nodded to Trump’s “America first” stance. “In international politics, we also deeply realize that we can’t just talk about values and not talk about interests. Of course, the United States must value its own national interests,” he added.
Experts say the US has become frustrated at having to shoulder the weight of other countries who fail to contribute to their own defense.
“The Trump administration has made clear its lack of tolerance. It’s had no tolerance for free riders,” said Thompson, from RSIS in Singapore.
“I think the countries that get that message clearest and fastest are the ones that are going to be the good partners of the United States, because it’s not like the US is abandoning allies. What the US is doing is prioritizing its most capable ones,” Thompson said.
This post appeared first on cnn.com